TELEMEDICINE – NEW LEAP IN HEALTHCARE

The healthcare industry mostly functions on physical interaction with a doctor-checking the pulse, using a stethoscope and diagnoses for the possible signs and symptoms. Now, such practices are largely suspended due to the coronavirus pandemic. The COVID-19 outbreak has created numerous challenges on traditional healthcare.
Due to worldwide lockdown, people have not been able to consult with doctors physically. This situation has made systems to change the regulations and accept the delivery of healthcare services and allow telemedicine via video, audio or text. Healthcare going digital seems more feasible than ever. Online consultations can prove to be a major relief for healthcare workers and patients.
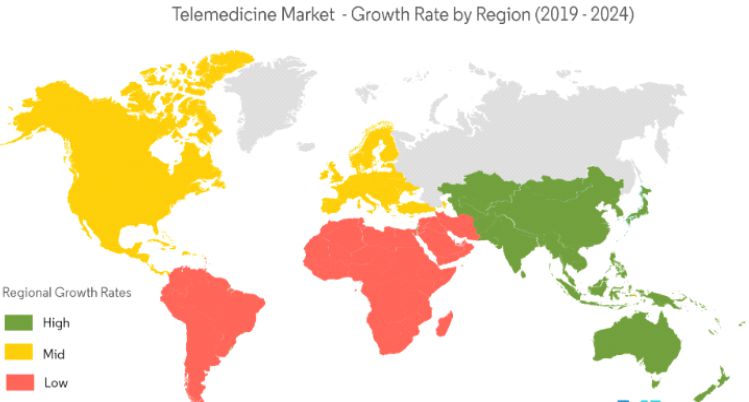
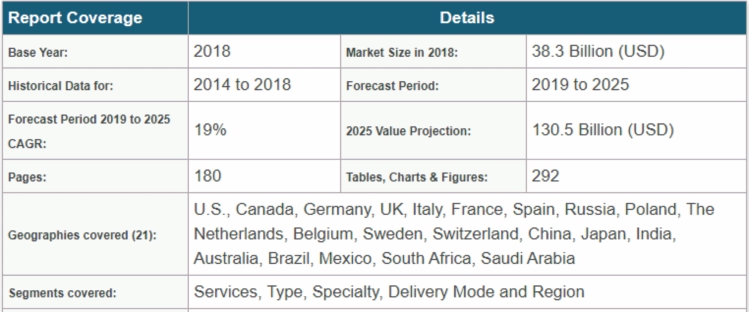
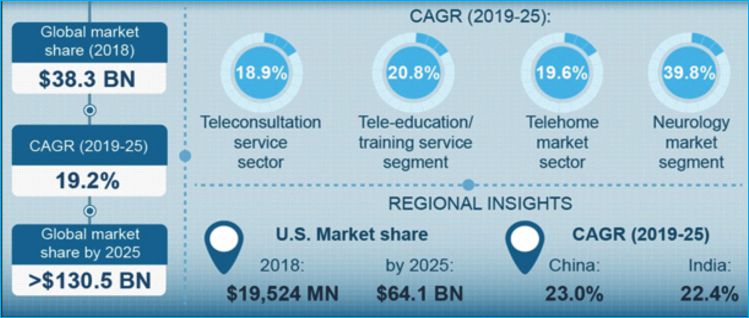
With the growing attention for telemedicine services, countries all over the world are developing a regulatory framework for the industry. Telemedicine market size was valued above USD 38.3 billion in 2018 and is expected to rise more than 19% CAGR from 2019 to 2025.

Growth Drivers
- Increasing prevalence of chronic diseases
- Growing number of smart phone users
- Technological advancements related to mobile phones and internet
- Greater need for cost saving in healthcare industry
- Long wait time in hospitals for treatment
- Favourable government initiatives
Service Segment, Region Share and Market Growth
Virtual presence is the new trend of technology pursued by the developed and developing countries, adopting through different systems including satellites, the internet, mobiles, wireless devices and media services. In the healthcare sector, virtual care acts as a platform for remote delivery of expert consultancy, detailed information and appropriate services to any desired location. Telemedicine is expected to increase market demand at a CAGR of 19.2% by 2025.
Current Indian Scenario
- Telemedicine market in India is expected to rise at a CAGR of 20% during FY16-20, reaching to US$ 32 million by the end of 2020
- Telemedicine can bridge the gap of rural-urban divide through the medical facilities, low-cost consultation and diagnosis facilities in the remotest of areas via high-speed internet and telecommunication
- Telemedicine is a fast-emerging sector in India; major hospitals (Apollo, AIIMS, Narayana Hrudayalaya) have adopted telemedicine services and entered into a number of PPP’s
Indian Growth Drivers
Despite the various initiatives undertaken by the government and private players, the Indian healthcare ecosystem faces numerous challenges and these challenges are the prime growth drivers in Indian market.
- Elderly population
- Government initiatives
- Shift in the disease burden (increase of chronic diseases)
- Inaccessibility to healthcare in the rural areas
- Manpower shortage
- Low insurance access
- Inadequate public sector investment and inconsistent quality standards
- Availability of high-speed digital network and hand-held monitoring devices
- Healthtech Startup’s in India and investments from VC’s
Startups such as Practo, DocPrime, mFine and Lybrate, have been operating telemedicine services in India under a regulatory area. The clarity in the regulations on telemedicine will not only help these startup companies to address the spread of coronavirus and it will also improve access to healthcare among the rural class.
Conclusion
There is a need for intervention and digital technology can be the game-changer and change the demography of the Indian healthcare. Telemedicine can bridge the existing gap and increase the accessibility and quality of healthcare by reducing the cost of healthcare. It can help bring down provider and patient costs as well as provide care in the most remote areas. Telemedicine can provide access to qualified healthcare providers, specialised consultations, timely diagnosis, effective course treatment to the rural population, hence bringing down the inconsistency in healthcare offerings between the rural and urban areas.

Dr Nageswar K
Group COO, OMNI Hospitals