Total Knee Replacement: A Step-by-step Guide to the Procedure & Recovery
Knee issues can have a profound effect on daily living and comfort, whether it’s caused by Arthritis, injury or the natural wear and tear that comes with aging, chronic knee pain can limit mobility, making even everyday activities like walking, climbing stairs or getting out of a chair incredibly difficult. When non-surgical treatments no longer provide relief, Total Knee Replacement (TKR) surgery offers a solution. This comprehensive procedure not only alleviates the pain but also restores mobility, allowing individuals to resume their daily activities with confidence.
If you or a loved one are considering Knee Replacement surgery, this step-by-step guide will walk you through the process and what to expect during your recovery.
What is Total Knee Replacement (TKR)?
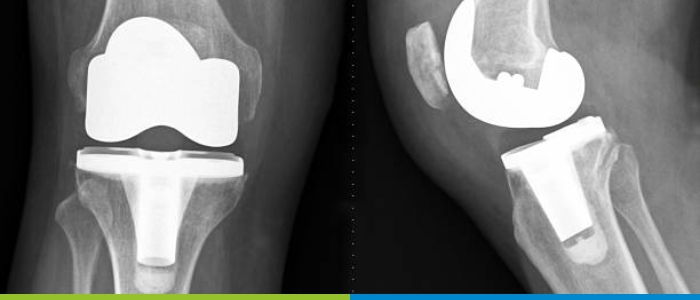
Total Knee Replacement (TKR), also known as Knee Arthroplasty, a surgical procedure in which the damaged or worn-out parts of the knee joint are replaced with artificial components. The knee joint involves the femur, tibia and patella, which are commonly known as the thigh bone, shin bone, and kneecap respectively. In patients with knee arthritis or significant knee damage, the cartilage cushions these bones and deteriorates, causing pain and stiffness. In TKR, the surgeon removes the damaged portions of the bones and replaces them with a prosthetic joint made of metal, plastic, and ceramic materials.
Step 1: Pre-operative Preparation
The journey to a successful knee replacement starts long before the surgery itself. Proper pre operative preparation is essential for ensuring a smooth procedure and optimal recovery.
Consultation with Your Orthopedic Surgeon
Before undergoing surgery, your Orthopedic surgeon will conduct a thorough evaluation to determine if you’re a suitable candidate for Knee Replacement. This includes reviewing your medical history, performing physical exam and ordering imaging tests like X-rays or MRIs to evaluate the level of knee damage. In addition, your surgeon will discuss your overall health, lifestyle and expectations, explaining the potential risks and benefits of the procedure.
Pre-Surgical Assessment
A pre-surgical assessment may involve blood tests, an electrocardiogram (ECG) and possibly a chest X-ray, especially if you have underlying health conditions. If you have chronic health issues such as Diabetes, Heart disease or High Blood Pressure, these are need to be managed before surgery to reduce the risks. Your surgeon will also discuss Anesthesia options, guide fasting and medication management before the procedure.
Step 2: The Surgery – What to Expect
Total Knee Replacement surgery typically takes 1 to 2 hours and usually performed under General Anesthesia, which means you will be asleep throughout the procedure. Some patients may opt for Regional Anesthesia, which numbs the lower half of the body but allows them to remain awake during the surgery.
Incision and Removal of Damaged Tissue
The surgeon begins by making an incision in the front of the knee to access the joint. The damaged cartilage and a small portion of the bone are removed from the femur and tibia. If necessary, the surgeon will also remove the damaged part of the kneecap (patella). The goal is to create a smooth surface for the artificial knee components to fix properly.
Implantation of Prosthetic Components
After removing the damaged tissue, the surgeon positions the prosthetic components. These include a metal component for the femur, a plastic component for the tibia and sometimes a plastic component for the patella. The artificial parts are carefully aligned to ensure they mimic the natural movements of a healthy knee joint.
Closure and Dressing
Once the prosthetic components are steadily in place, the surgeon will close the incision using stitches or staples and apply a sterile dressing to the wound. In some cases, a drain may be placed temporarily to remove excess fluid or blood from the surgical site.
Step 3: Post operative Care and Immediate Recovery
Following the surgery, you will be shifted to the Post op ICU in general terms recovery room, where your vital signs will be monitored closely as the anesthesia wears off. You may feel groggy or disoriented immediately after the procedure, but most patients experience minimal pain thanks to the use of pain management techniques, such as nerve blocks or medication.
Pain Management
Pain control is a critical part of the recovery process. Pain management will be provided through prescribed medication from your Doctor. In addition to drugs, your healthcare team may use ice packs or elevate your leg to reduce swelling. Staying ahead of pain in the early days after surgery is important, as it can make rehabilitation exercises easier.
Physical Therapy and Early Mobility
Physical therapy begins as soon as the day of the surgery. It may sound daunting, but moving the knee early is essential to prevent stiffness and promote healing. Your physical therapist will guide you through simple exercises to improve knee flexibility and strength. You may be asked to start walking with the help of a walker or crutches.
Step 4: The Recovery Process – What to Expect
Hospital Stay
Most patients stay in the hospital for 2 to 3 days after the surgery. During this time, you’ll continue with pain management, physical therapy and mobility exercises. The healthcare team will monitor your progress and ensure that there are no complications, such as infections or blood clots.
At-Home Recovery
Once discharged from the hospital, you’ll continue physical therapy at home or an outpatient rehabilitation center. At this stage, you’ll gradually increase your activity level. Although you’ll likely need assistance for the first few days, most patients can resume normal activities, such as walking short distances, within the first few weeks.
Long-Term Rehabilitation
Recovery always varies from person to person, but it typically takes 6 months to a year to regain full function. Rehabilitation is essential for reaching the optimal recovery outcome. This will involve continued physical therapy to strengthen the muscles surrounding the knee, improve joint flexibility and enhance overall mobility.
Step 5: Lifestyle Adjustments and Long-Term Care
Lifestyle Modifications
After a full recovery, you’ll be able to return to many of your normal activities. However, it’s important to avoid high-impact sports and activities that could put undue stress on the new knee. Maintaining a healthy weight and staying active with low-impact activities such as swimming, cycling and walking will help prolong the life of the prosthesis.
Monitoring the Knee Implant
While a knee replacement is designed to last many years, it’s essential to follow up regularly with your orthopedic surgeon. Over time, the prosthetic components may wear out and you may require a revision surgery. Staying active and keeping the surrounding muscles strong can help ensure the long-term success of the procedure.
Conclusion
Total Knee Replacement surgery is a highly effective solution for individuals with chronic knee pain who have not found relief from non-surgical treatments. By following the step-by-step process outlined in this guide, you can gain a better understanding of what to expect before, during, and after the procedure. With proper care, rehabilitation and lifestyle modifications, knee replacement patients often experience significant pain relief and a return to an active, fulfilling life.
If you’re considering Total Knee Replacement, consult with an experienced Orthopedic surgeon to determine if you’re a good candidate for the procedure. Take the first step toward a pain-free future today!
